The article was consulted professionally by ThS.BS Hoang Quoc Hoang – Share99 Research Institute of Stem Cell and Gene Technology.
Families with children with birth defects often wonder why their child has it? And will their next children suffer from these deformities? Abnormalities in heredity can be transmitted from parents to children. This article is intended to provide more information to answer questions about genetic disorders and birth defects, as well as to introduce genetic mutation screening tests and birth defect detection tests.
1. What is a gene?
Genes are a unit of genetic matter that has the smallest function. Genes contain information necessary for the formation, development and functioning of an individual. Genes are understood as a recipe which contains all the information necessary to create a certain dish. Each gene will have two copies, one from the father and one from the mother.
2. What are chromachromia?
Chromochromochroma is a genetic structure that contains a set of many genes. Chromotypes are likened to a chapter of books and each article in that chapter is a gene. Chromaties also exist in similarities in nourishing cells. Each nourishing cell contains 46 chromaties and is divided into 23 pairs of similar chromaties consisting of 22 pairs of common chromaties and one pair of sex chroma . Sperm and egg cells are reproduction cells so there are only 23 single chromatosis (one chromatosis of each pair is similar). When sperm is combined with eggs during fertilization, 23 chromatosis from the father will pair with 23 similar chromaties from the mother to create a complete set of chromaties.
3. What regulates the sex of the baby?
The sex of the baby is determined by the presence of sex chroma. There are two sex chroma, X and Y. Egg cells have only X chroma while sperm cells may contain X chroma or Y chroma. When eggs and sperm come together to produce chroma containing the XX or XY chroma. The chroma containing the XX chroma will develop into a girl while the est prince containing the XY chroma will develop into a boy.
4. What is a genetic mutation? What is chroma disorder?
Genetic mutations are a consequence of structurally abnormal variations and/or the number of genes.
Chroma disorder is a consequence of structurally abnormal variations and/or the number of chroma. Most babies born with chroma disorder have er dyschromic defects and in some cases have intellectual defects. The risk of giving birth to a child with chroma disorder increases as the mub age increases.
Trisomy is a disorder of the number of chromaties in which a nourishing cell has 3 similar chromaties rather than two chromaties that are similar to normal cells. The most common trisomy is the addition of a chrom chrom chroma no. 21(Down's disease). Other common trisomies are the addition of chromo chromost 13(Patau syndrome)and the addition of chromochromo symptom No. 18 (Edwards symptom).
Monosomy is a disorder of the number of other chromaties in which nourishing cells remain only one chromatomy instead of two chromaties similar to those in normal nourishing cells. Loss or damage to the X chroma is a common monosomy and is the cause of Turner syndrome.
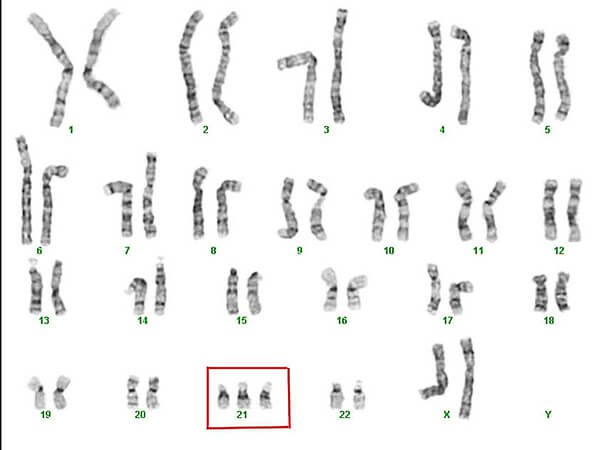
5. What is genetic disorders?
Genetic disorders are a consequence of genetic mutations transmitted from parents to children. Genetic mutations can occur in any chromosomes. Genetic disorders are divided into dominant genetic disorders and diving on common chroma, and sex-linked genetic disorders.
What is dominant genetic disorder on chroma?
Dominant genetic disorders on chromosomes are usually disorders caused by only one abnormal gene that the child inherits from the father or mother, that is, the child will get sick if one gene in the pair of similar genes is muted and the other remains normal. If a parent has an abnormal gene, their children have a 50% risk of carrying similar abnormalities because 50% of their genome is inherited from their father and the remaining 50% is inherited from their mother. An example of a dominant genetic disorder on chroma is usually the disorder that causes Huntington's disease.
What is a heredity of diving on chroma?
Dive genetic disorders are disorders that occur only when both parents carry the same abnormal gene, that is, the child is sick only when inheriting both abnormal genes, one comes from the father and one comes from the mother. The child will not show any abnormalities if the child carries only one abnormal gene of a pair of similar genes, that is, in two similar genes only one gene is muted. An example of a heredity that dives on chroma is usually the disorder that causes cystic fibrosis.
What is a diving genetic mutation?
The genetically mutable carrying body is a person with a pair of genes that are not similar, that is, two genes in the pair of similar genes are not the same, one is muted and the other is normal. People carrying a genetic mutation may not have any symptoms of illness or are very mild. If both parents are carrying a genetic mutation, their child will have a 25% risk of illness from a diving genetic disorder and a 50% risk of being able to carry a genetic mutation – just like the child's parents. If only the parent is a person carrying a genetic mutation, the child has a 50% risk of being able to carry a genetic mutation.
What is sex-linked genetic disorder?
Sex-linked genetic disorders are disorders caused by mutations of genes located on sex chromosomes (X and Y). An example of sex link disorder is hemophilia. This is a disease caused by a genetic mutation located on the X chromotype.
Who is at risk of giving birth to a child with birth defects?
Most children with birth defects are born to parents who do not have any risk factors. However, the risk of birth defects is higher in people with risk factors. Screening for birth defects should begin by checking if you carry any risk factors? Like do you have a genetic mutation? Do you have children with genetic mutations, or do you have a family history of genetic disorders? Some genetic disorders occur more often in certain human populations.
What is genetic counseling?
In some cases, you may be advised to see a genetic consultant. Genetic consultants are highly trained in genetics. Besides learning about your family's medical history, a genetic consultant may recommend going to the doctor and getting tested. Based on this information, your genetics consultant will assess the risk of birth defects to your child, discuss with you your options, and answer your questions.

What types of pre-birth tests can answer your questions about genetic disorders?
Pre-birth screening assesses a child's risk of birth defects or genetic disorders.
Diagnostic tests can detect specific birth defects or genetic disorders of the fetus.
When should pre-birth filtration be carried out during pregnancy and the type of mobility disorder evaluated?
Pre-birth screening is usually part of the process of maternity health care and is usually carried out at different times throughout pregnancy. Pre-birth screening consists of examining certain substances in the blood of the pregnant woman and ultrasound. These tests assess the risk of down and other trisomies, as well as fetal nervous tube defects.
What is a genetic mutation-carrying test?
A genetic mutation-carrying test is a filter-to-filtration test that determines whether a person carries a genetic mutation.
Who should take a genetic mutation test?
Genetic mutation-carrying testing is generally recommended for individuals with a family history of genetic disorders or for high-risk populations with certain genetic disorders. Pregnancy testing with cystic fibrosis is generally recommended for all women of child sexual age because it is one of the most common genetic disorders.
When to perform a genetic mutation test?
Genetic mutation pregnancy tests can be performed before and during pregnancy.
When will diagnostic tests be performed during pregnancy and what abnormalities are detected?
Diagnostic testing can be performed where the screening test in turns out a high risk for birth defects. Diagnostic testing may also be recommended for all pregnant women, even those who are not at risk. Diagnostic tests can detect certain birth defects or genetic disorders.
How is diagnostic testing performed?
Serious diagnostic consideration is carried out on cells originating from the fetus. These cells are present in amniotic fluid and vegetable spikes, or, rarely, from the blood of the fetus. Chromotypes and genes in these cells will be analyzed using laboratory techniques to diagnose certain genetic defects.
What are the risks of diagnostic testing?
Diagnostic testing carries certain risks including pregnancy.
How do I know which test is appropriate?
Your doctor or genetic consultant can provide information about the types of tests and help you choose the right test based on your personal risk factors.
Do I really need to do these tests?
It is your right to perform the test. Some couples don't want to know about their child's risk of carrying birth defects, but others want to know these risks in advance. Knowing in advance about the risks will give you time to prepare your child for specific malformations and to prepare for the medical assistance they may need. You can also choose not to continue your pregnancy.
- Does pre-pregnancy screening help detect genetic disease genes?
- What is Aarskog-Scott syndrome?
- Can the loss of the segment on the Y chroma give birth and what risks are there?

